fDet
Introduction
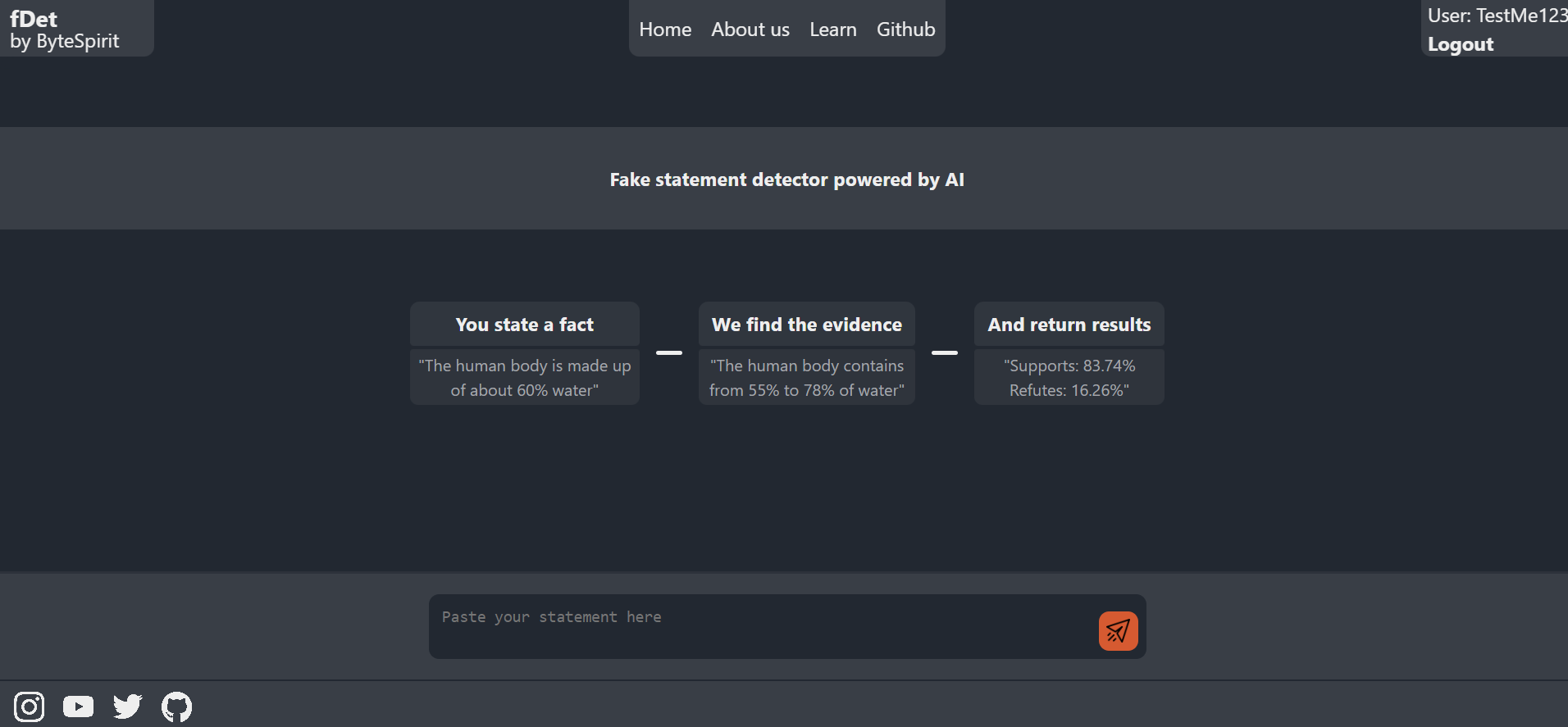
This project focuses on the development of an application designed to detect false information using an AI algorithm connected to reliable sources, such as Wikipedia. The primary objective is to create a fast and user-friendly system for verifying claims, accessible to the general public.
Goal of the project
The goal of this project is to build an application that effectively detects and verifies the authenticity of claims by searching reliable information sources. It should deliver accurate results quickly while remaining cost-effective and logical in reasoning.
My approach
I contributed to the design and development of the machine learning solution for detecting false information. To achieve this, I focused on creating an AI algorithm capable of analyzing and verifying claims using trusted sources like Wikipedia. To address the challenge of efficient document retrieval, I initially experimented with the DPR (Dense Passage Retriever) model, which delivered satisfactory results in finding and providing logical evidence for claims. However, due to response times of over 15 seconds, I implemented the Okapi BM25 algorithm, which reduced response time to under 3 seconds. To further improve the system, I integrated the RoBERTa language model for classification due to its balance between performance and hardware efficiency. I used the PyTorch framework for fine-tuning the model, leveraging datasets like HoVer and FEVER. Despite achieving 89.3% accuracy on test datasets, limitations with number handling and advanced reasoning persisted. To overcome these issues, I integrated the GPT-3.5 model via OpenAI's API, requiring prompt engineering adjustments while maintaining system efficiency.
Result
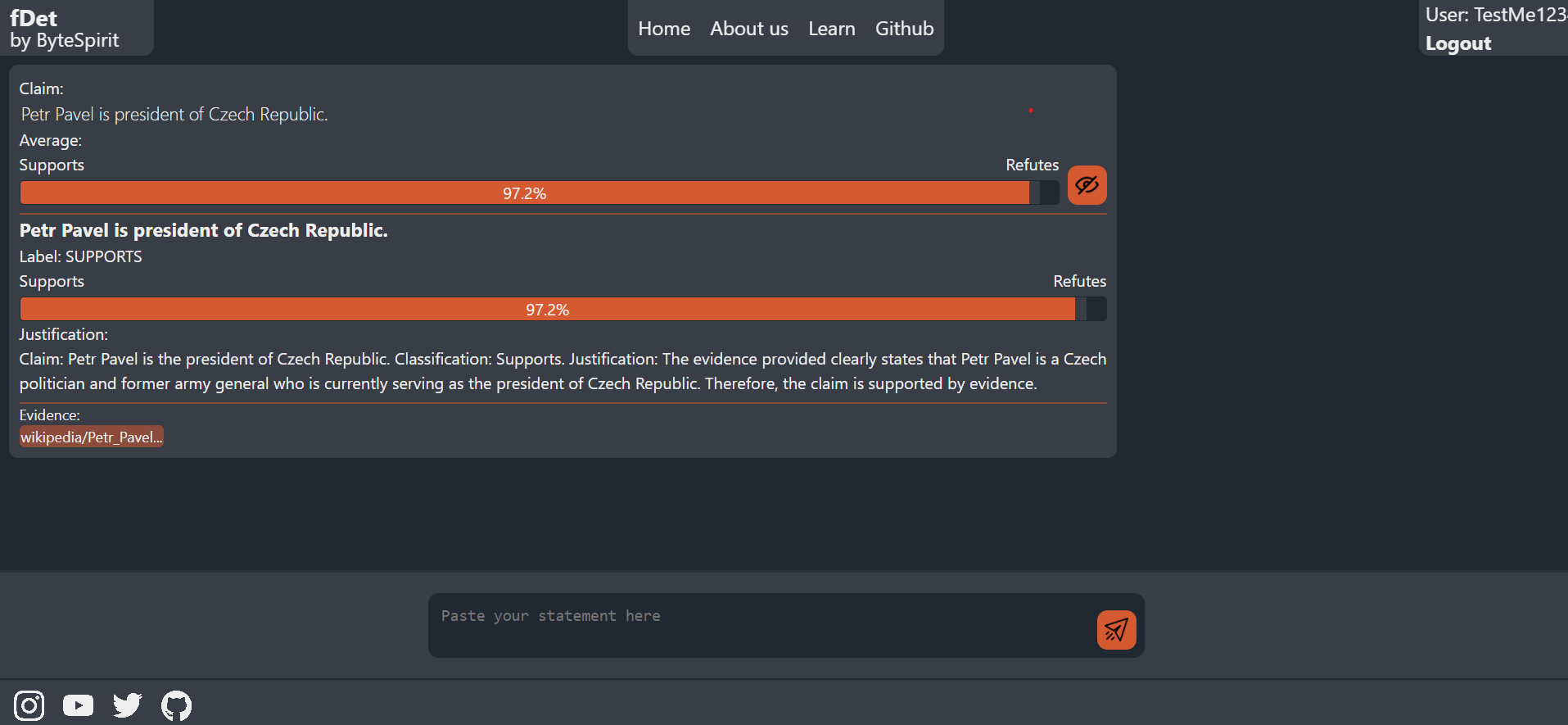
The project successfully verified basic claims such as 'Dog has four legs' and more contemporary topics, providing logical explanations for claim validity.
Photos